Demyelination – a term that might sound like scientific jargon but has real-world implications for many. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and a
Demyelination – a term that might sound like scientific jargon but has real-world implications for many.
Understanding its symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for everyone, not just those directly affected.
What is demyelination?
Demyelination occurs when the protective covering of nerve fibers in the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves, known as myelin, is damaged.
This myelin sheath facilitates the rapid transmission of electrical signals. When it’s compromised, nerve signals slow down or stop, leading to a range of neurological symptoms.
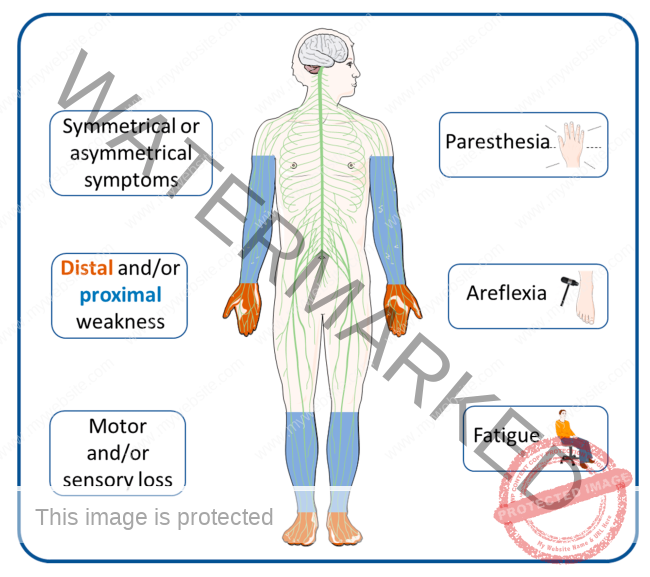
Symptoms
- Visual disturbances: This can include blurred vision, double vision, or partial vision loss. Some individuals may experience a condition known as optic neuritis, which is inflammation of the optic nerve causing painful vision loss.
- Muscle weakness: Affected individuals might find it difficult to perform everyday tasks due to weakness in one or more muscles.
- Numbness or tingling sensations: These sensations can occur in any part of the body and are often among the first signs noticed.
- Coordination and balance problems: This may manifest as difficulty walking, unsteadiness, or clumsiness.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of exhaustion that isn’t relieved by rest.
- Dizziness: Some people may experience episodes of dizziness or feel as though their surroundings are spinning (vertigo).
- Cognitive issues: These can include problems with concentration, memory, and processing information.
- Emotional changes: Mood swings, depression, or euphoria can occur.
- Heat Sensitivity: Symptoms may worsen with increased body temperature.
- Bladder and bowel problems: This can include increased frequency, urgency, or incontinence.
Causes
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most well-known cause of demyelination, but it’s not the only culprit. Other causes include inflammatory diseases, infections, and immune-mediated conditions.
Sometimes, the exact cause remains a mystery, which can make managing the condition challenging.
Treatment options
While there’s no cure for demyelination itself, treatments aim to manage symptoms, reduce autoimmune attacks on the myelin, and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Options include medication to reduce nerve inflammation, physical therapy to enhance mobility, and lifestyle adjustments to minimize symptom triggers.
Prevention
Preventing demyelination begins with understanding risk factors and taking steps to mitigate them. Although not all causes are preventable, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing chronic conditions, and avoiding known triggers can help.
Regular check-ups and staying informed about symptoms can lead to early detection and treatment, potentially reducing the impact on one’s life.
Demyelination might sound daunting, but knowledge is power. Recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, and exploring treatment options are key steps in managing this condition.
By staying informed and proactive, individuals can navigate the challenges of demyelination with confidence and support.
COMMENTS