Deafness, a condition affecting millions worldwide, can significantly impact one's quality of life and communication abilities. From congenital ca
Deafness, a condition affecting millions worldwide, can significantly impact one’s quality of life and communication abilities.
From congenital causes to acquired conditions, understanding the underlying factors, available treatments, and effective management strategies is crucial for individuals living with deafness and their caregivers.
Let’s delve into the multifaceted world of deafness to shed light on its causes, treatment options, and practical management approaches.
Causes of deafness
Deafness can arise from various factors, both congenital and acquired. Congenital deafness may be due to genetic abnormalities, maternal infections during pregnancy, or complications during childbirth.
Acquired deafness can result from exposure to loud noises, aging (presbycusis), infections (such as meningitis or otitis media), traumatic injuries, or certain medications (ototoxic drugs).
Understanding the specific cause of deafness is essential for determining appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Treatment options
Treatment options: The treatment of deafness depends on its underlying cause and severity. For individuals with conductive hearing loss caused by problems in the outer or middle ear, treatment options may include medication, surgical procedures (such as tympanoplasty or stapedectomy), or the use of hearing aids to amplify sound.
Sensorineural hearing loss, affecting the inner ear or auditory nerve, may require cochlear implants, which bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve to provide sound perception.
In cases of profound deafness or when traditional treatments are ineffective, sign language and communication therapies can help individuals adapt to their hearing loss and enhance their communication skills.
Management strategies:
Effective management of deafness involves a comprehensive approach that addresses the physical, emotional, and social aspects of living with hearing loss.
Communication strategies, such as lip-reading, sign language, and assistive listening devices, can facilitate effective communication and social interaction.
Educating family members, friends, and caregivers about deafness and communication techniques can foster understanding and support for individuals with hearing loss.
Access to educational resources, vocational training, and support services, including counseling and advocacy groups, can empower individuals with deafness to lead fulfilling and independent lives.
Additionally, incorporating environmental modifications, such as installing visual alarms and captioning services, can enhance accessibility and safety for individuals with hearing loss in various settings.
Deafness is a complex and diverse condition that requires tailored approaches to treatment and management.
By understanding the underlying causes of deafness, exploring available treatment options, and implementing practical management strategies, individuals with hearing loss can overcome challenges and thrive in their personal and professional lives.
Embracing inclusive practices, promoting awareness and education, and fostering supportive communities are essential steps towards creating a more accessible and inclusive society for individuals with deafness.
Together, we can break down barriers and celebrate the resilience and diversity of the deaf community.
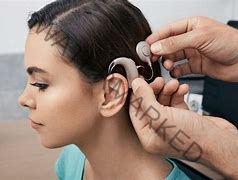
COMMENTS